Multiuser communication allows multiple point-to-point (peer) connections between multiple instances of Packet Tracer. By allowing communication between Packet Tracer instances, a new door has been opened to a fun, interactive, social, collaborative, and competitive learning environment. Instructors will now be able to create a variety of activities for students to learn in groups that will facilitate greater social interaction between students. Students will benefit from this environment by working together to solve problems and share ideas. Both students and teachers should take full advantage that Multiuser will offer in their learning environment.
Technical Information
- Communicates between instances using PTMP.
- PTMP is TCP based.
- By default, uses TCP port 38000, is customizable, and each new instances on the same PC will use the next available port.
- On by default.
- UPnP will attempt to establish port forwarding to facilitate home networks.
- All network communication allowed between instances.
- Console cable also allowed.
- Transparent to the simulated network.
- Default password: cisco
- Wireless is not supported over Multiuser.
Dialogs
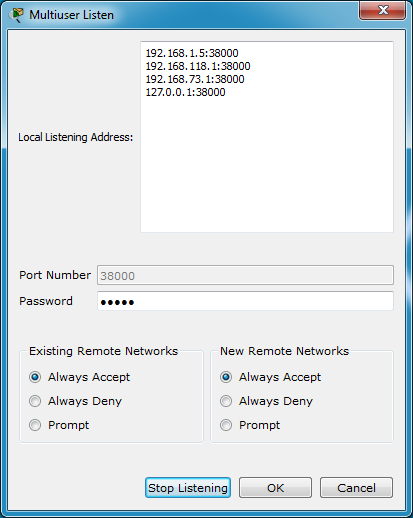
Multiuser is on by default, users who wish to turn this feature off may do so in the Extensions > Multiuser > Listen menu. The server settings can be configured from this dialog. The default password is "cisco", it is highly recommended to change this password. To configure the port number, click Stop Listening and then change it and click Listen again.
Existing Remote Networks refers to multiuser connection clouds that already exist on your desktop. The options allow the user to Always Accept a remote connection request with no prompt, which is very handy in gaming and central connection scenarios. The second option will Always Deny connections, refusing any connectivity to existing multiuser clouds on the desktop. The third option Prompts the user on the receiving side of the connection to manually accept or deny the connection.
New Remote Networks supports the same three options as the previous option. The key difference is that the multiuser clouds don't yet exist on the receiving user's workspace. If the option is set to Always Accept a new multiuser cloud is created on the workspace and connection to the initiating copy of Packet Tracer is established. If the option is set to Always Deny nothing happens as the connection is refused. If the option is set to Prompt the user on the receiving side of the connection to manually accept or deny the connection, if accepted a new multiuser cloud is created on that user’s workspace.
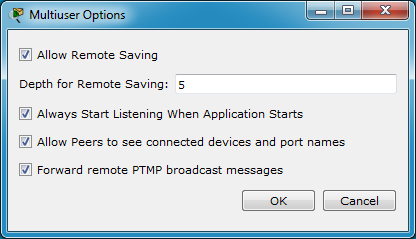
The Extensions > Multiuser > Options dialog can be used to configure other settings. Allow Remote Saving controls whether this network can be saved from a remote network using offline saving. Depth for Remote Saving configures how far deep into the remote user sessions will be saved. For example, if the users are connected as such:
A <=> B
B <=> C
C <=> D
D <=> E
E <=> F
F <=> A
If A is configured with a depth of 2 and attempts to offline save, A will receive a copy of B, C, E, and F's networks, but not D's. Always Start Listening When Application Starts controls whether Multiuser will be on or off during startup. Allow Peers to see connected devices and port names controls whether the remote user will see the device name and port name when they create a cable connection to your networks. Forward remote PTMP broadcast messages works in conjunction with Packet Tracer External Applications (ExApps). Its function is to allow the ExApp to communicate with all connected copies of Packer Tracer. This option has no effect on the Packet Tracer program by itself.
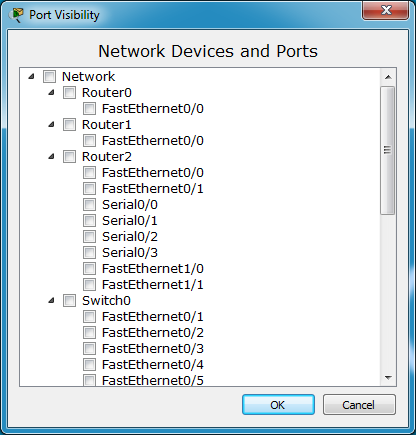
Port Visibility
The Port Visibility dialog allows you to control what ports on which devices in your network will automatically show up as an available port on connected remote peer's networks. The remote peer can connect to these ports without requiring your end to create the link.
Connection States
Multiuser has four different connection states. The Multiuser cloud is in the Disconnected state when there is no remote network connection to a remote peer. The Multiuser cloud goes into the Connecting state when a request is sent to a remote peer to make a remote network connection. When two remote peers make a remote network connection, the Multiuser cloud goes into the Connected state. The Error state indicates there is a remote network connection error with the remote peer. For example, if the remote peer's connection suddenly lost network connectivity, then the Error state would appear.
User Guide
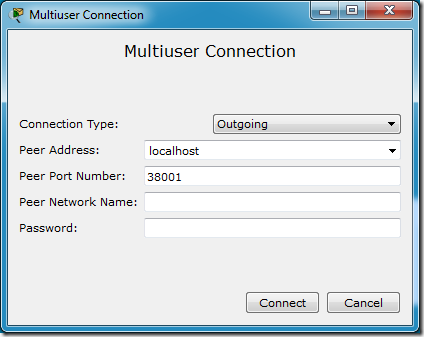
To create a Multiuser connection to another user, click on the Multiuser Connection in the Device-Type Selection Box. Then select the Remote Network cloud and create it on the workspace. This cloud will represent one entry point to another user. Multiple multiuser entry-points to the same user are allowed. Click on the cloud to open the Multiuser Connection dialog.
To create an outgoing connection, choose the Outgoing option for Connection Type. In the Peer Address field, enter the remote user's IP address and the port their instance of Packet Tracer is listening on in the address:port format. Peer Network Name is optional. The option allows this outgoing connection to connect to a specific incoming cloud the remote peer has set up. For example, if the remote peer created an Incoming connection cloud named Routers, then you can enter Routers in this field and it will connect to the Routers cloud in the remote peer's network. Leaving this field blank will create a new cloud in the remote peer's network. The new cloud will have the same name as the cloud that initiated the connection unless that name already exists, and then the name will be incremented to the next available “name+number”. The password field is the password set in the Listen dialog from the remote peer's Packet Tracer instance. When the fields are set properly, click on the Connect button.
When an incoming connection happens, you will be prompted (by default, but can be changed under Extensions > Multiuser > Listen) to accept this connection. When the incoming connection has been accepted, a Multiuser session has started. Each peer will have a cloud for connecting a cable to the remote user. This cloud can be thought of as a universal patch panel. Both users must establish a connection to this cloud to create a link between two remote devices.
To create a link between devices, it is very similar to a normal connection, except the other user must also make the connection. Start by selecting a connection type in the Device-Specific Selection Box, and create the link to your device on one end, and select the cloud on the other end. As with clusters, automatic connections are not allowed with Multiuser clouds. When you click on the cloud, a popup list similar to the list of ports in a device will appear. The first option will be Create New Link, and subsequent items will be available ports. Create New Link will connect your cable to the cloud as one side of a cable run. If ports are available, it means the other user has cables connected to their end of the cloud and you may connect to these ports. Connecting to one of these available ports will establish a fully connected cable between remote devices.
Offline Saving
There are now two options for saving networks. The normal Save in the Menu Bar and Main Tool Bar will create a save file with only your network and any remote peer connections will be saved as a remote peer connection. Offline Saving will save your network and remote peer networks as a cluster into a single large network. Offline Saving is controlled by the Depth for Remote Saving that you set and the permission the remote user set. Opening up a normal save file with a remote peer connection will cause Packet Tracer to attempt to reconnect these remote peer connections. Opening up an offline saved network will be a regular network with clusters for remote peer networks. Offline Saving is useful to examine others' networks or to use Simulation Mode.




This seems a bit outdated. I have rather used the prep material from exams.cf/cisco/
ReplyDeleteWorked very well!
I fully agree with the latest commentary. The information should be updated, as the data is too old and cannot be considered correctly.
ReplyDelete